By Ujjwala Karle
The automotive industry is constantly evolving. The global trends that define the top technology basket of mobility are Connected, Automated, Shared and Electrified (CASE). For India CASE will be modified to include nation-specific needs. Loaded with these features the new tagline will be Software Defined Vehicles.
Of all the global trends and terminologies of the future, two most impactful factors will be the two zeros: Vision Zero… zero accident deaths, and Carbon Zero… carbon neutrality and circularity.
To ride along with these global factors, the Mobility CASE for India gets modified and can be defined as: C – Connected & Shared to address congestion, A – Affordable & Accessible to reach the masses, S – Safe & Secured to minimize accidents, and E – Environment friendly & Energy independence.
Disruptive solutions
The disruptive solutions for the Indian CASE and the two global Zeros will depend on technologies such as Digitization, Connected vehicles, Alternative fuels, Automation, and Advanced materials and processes.
Digitization: Digitization is going to affect the entire life cycle of vehicles from design, validation, manufacturing to after sales service. Digital tools to conceptualize and design the unknown are not new to the industry. Integrated computational material engineering will soon be a common practice to optimize new materials, processes, design, manufacturing and validation methods. Creating digital twins for various systems and subsystems in different domains will enable this value chain. Industry 4.0 is a key for further digitization and customization in manufacturing. Industry 5.0 is round the corner, which talks about renewable fuels and human interventions with cobotics, (defined as a robotic device designed, manufactured and used to interact and cooperate with a human.)
A strong back-end connectivity and services are enabling trends and technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These are expected to have a significant impact on the automotive industry, enabling new business models and services.
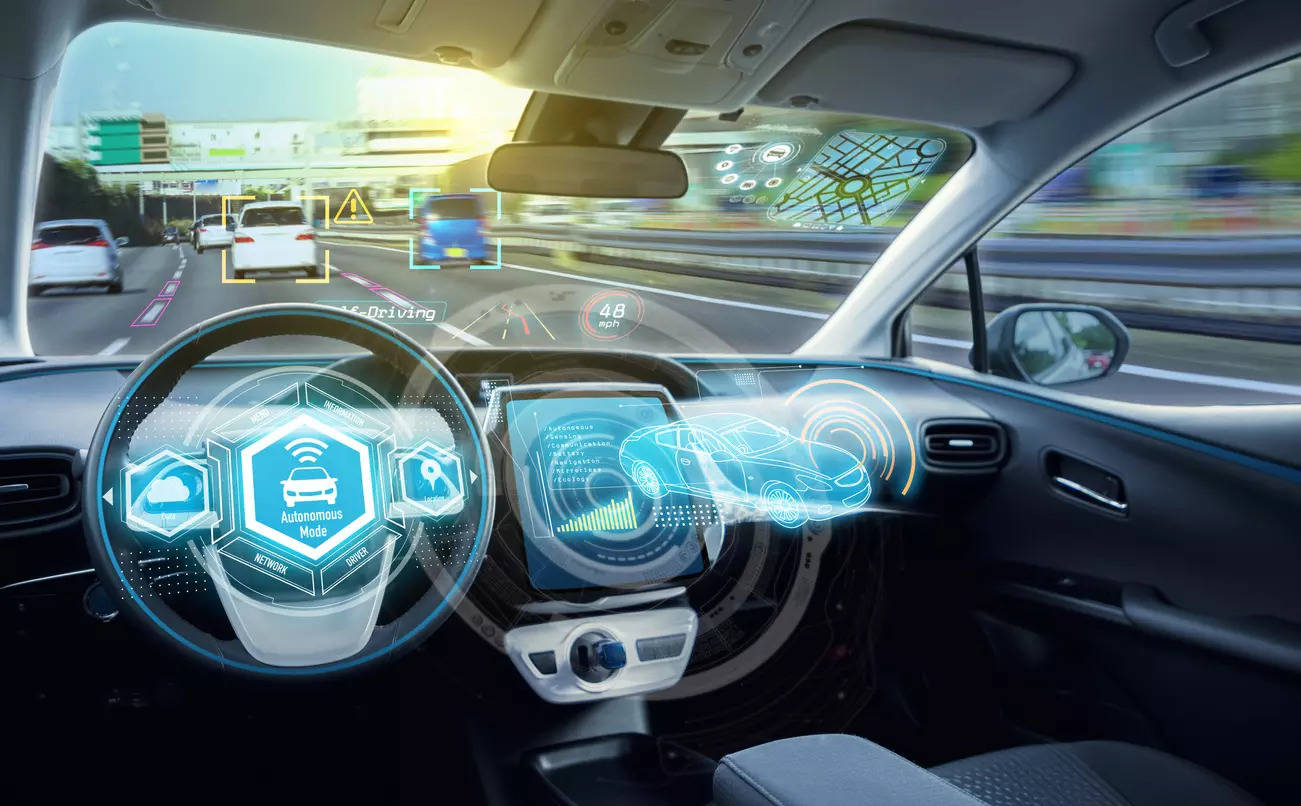
Connected vehicles: Thanks to digitization, vehicles will soon have features that can communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and the internet (V2X). They can exchange information such as traffic conditions, weather, and road hazards to improve safety and efficiency. V2G technology enables electric vehicles to store energy and feed it back into the grid when needed.
As connectivity-based solutions become differentiating factors, there is increased need for cybersecurity measures to protect against potential cyberattacks. Vehicles rely on advanced software systems and communication networks to operate, and these systems are vulnerable to hacking and other forms of cybercrimes such as compromising the safety of the vehicle and its passengers, or even causing accidents. This calls for a range of measures, such as secure software development practices such as DevOps, encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection and prevention.
Locally available green alternative fuels:Biofuels with variable blending mix, Compressed Biogas (CBG), Hydrogen blends are a few examples with the current ICE technology. While fuel cell technology is apt for EVs, which have zero-emission potential, the battery technologies beyond current Li-Ion technologies with higher energy density, longer life, better temperature performance, higher recyclability and using locally available materials are a challenge to address. Renewable energy generation with solar /wind/ hydro power will be key for EV charging infrastructure. Thus, life cycle analysis from cradle to grave will enable the right energy mix, which is local.
Autonomous vehicles: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous functions will be one of the important technologies for marching towards vision zero. These are the functions, which will recognize and act in case of Indian scenarios and use cases with varied infrastructure, vehicle classes, multiple languages, on-road behaviour of drivers and vulnerable road users.
Advanced materials and processes: Sustainable composites with different fibre mixture, nano materials, aluminium-magnesium alloys will find more applications for right weighting. Additive manufacturing processes will change the landscape of not only developing the products but also tooling and fixtures. Materials like High Entropy alloys will find applications in coatings and wear resistance materials. Beyond that there will be many more materials for energy storage systems like graphene, carbon nanotubes, silicon and rare earth-free magnets for motors etc.
Overall, the future of the automotive industry is likely to be shaped by a combination of these and other emerging technologies.
Effective collaborations
As the technologies are getting updated dynamically to have the disruptive solutions to keep the pace of the same and to move one step ahead of curve:
·It is no more working in silos, it is all about effective collaborations “TOGETHER WE CAN”; thus, synergising the strengths of one another.
·The key part will be to have good systems engineering knowledge and design thinking tools and acumen, as the challenges are now multidomain, multi-entrant and multifaceted and that call for boundaryless engineering.
·Learnability to adapt to new techniques and technologies and to un-learn quickly.
·Enablement and empowerment of ‘4I’ model, nurture ideas, help them to implement, uplevel them to be market-ready products/ solutions to ensure innovation to create a bigger and deeper societal impact.
Technology is global, but solutions are local. Learn from global experiences, and create your own solutions.
While achieving the above, there is a great opportunity to attain Infinity: Infinite innovation, youth engagement and global manufacturability.
The Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) enables synergizing the technologies for emerging mobility CASE through E3 – Expertise, Experience and Equipment.
(Disclaimer: Ujjwala Karle is Deputy Director and Head — Technology Group, Automotive Research Association of India. Views are personal)