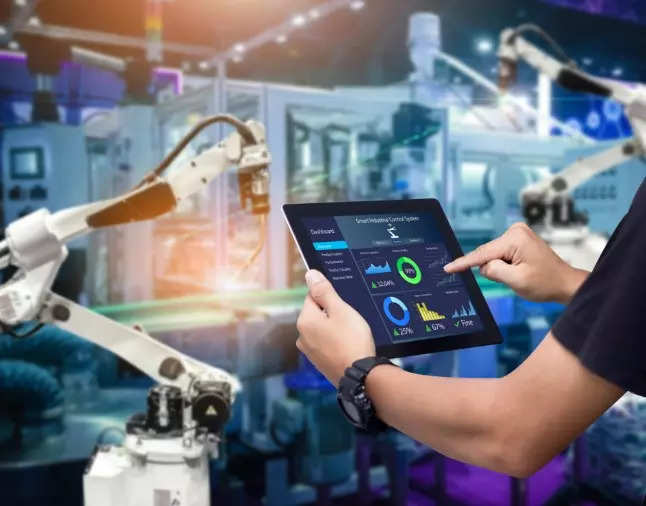
Robots are the executors of whatever task they are designed for, meaning they are only as powerful as the underlying algorithms used to program them. Machine learning harnesses the power of data to enable perception and decision-making in complex situations. Self-driving cars are perhaps the most popular example. These rely on machine learning algorithms to navigate roads and make real-time decisions, such as swerving to avoid a possible collision. In industrial automation and manufacturing, machine learning is used to run a tighter and more efficient supply chain by enabling systems to take decisions autonomously. One of the main use cases is predictive maintenance. This involves using data to predict when a piece of equipment is likely to fail and proactively schedule repair work, thereby saving on maintenance costs and reducing the equipment’s downtime. Smart warehouses leverage ML to gain real-time visibility, automate processes and spot gaps or opportunities in warehouse management- saving time and cutting costs.
Robotics is changing the healthcare and diagnostics industry in a big way too. At the most superficial level, robots can perform maintenance tasks like disinfecting patient wards and transporting items. But when powered with AI and ML, robots can assist in performing precise surgical procedures, analyze medical images to identify tumors or fractures, offer diagnosis based on symptoms and medical history, and much more.
Precision medicine is a burgeoning field where ML and robotics are being leveraged to conduct medical profiling for highly specific groups of patients and providing them tailored medical solutions. On the administrative side, many healthcare businesses are investing in autonomous robots that can check patients into the clinic or accompany physicians on their rounds as a way to bring in second opinions from remotely based specialists. These robots can also offer remote medical diagnostics, particularly for locations that are difficult for healthcare workers to access on foot, such as a flooded area or a building struck by an earthquake. Other applications include medical transcriptions, translating languages (including sign language) and generating electronic health records. In short, machine learning enables robots to be smart, diligent and round-the-clock aides to physicians, leading to much higher efficiency in an overworked healthcare system. Enabling technologies, techniques
The link between machine learning and robotics can be summarized as – machine learning trains the robot to become smart enough to perform tasks on its own.
In the early days of robotics, this took the form of hand-crafted machine-learning algorithms. More recently, however, the focus has shifted to deep learning that can analyze and interpret data automatically. This can range from simple classification models (such as training robots to identify and classify objects based on visual inputs) to advanced applications like generative AI, attention-based sensor fusion or multi-domain models. Deep learning enables exponential progress in terms of perception and cognition in robots, making it easier for humans and robots to interact and work safely together.
Future prospects and concerns
Machine learning holds immense potential for every industry – there are bottlenecks, however, to applying it at scale. For instance, complex applications involve the use of multiple machine learning models simultaneously, which not all companies may have the processing capacity for. There’s also the fact that the models are continuously increasing in size and scope to accommodate new data. Another issue relates to data handling at the pre-processing stage – if not executed swiftly or efficiently enough, it could lead to pipeline bottlenecks and potentially feed out-dated or incorrect data to the algorithm. There are also data privacy concerns about using the cloud, especially when it comes to sensitive datasets like medical records or financial histories.
The way forward
Objectively, robotics holds an immense amount of potential. The challenge lies in figuring out ways for robots to be used at scale and without interfering with human decision-making. Smart factories are already recruiting AI-powered robots to work on routine tasks and handle the heavy lifting – something they can do much more safely and efficiently than humans can. Hospitals are also opting for robotic assistance more and more, as are security companies and the customer service industry. Going forward, we can expect machine learning and robotics to become more collaborative as more and more industries opt for automation. Innovative solutions will pave the way for new leaps in machine learning deployment, which will translate to the mass application of robotics to solve long-standing and emerging challenges. Exciting times lie ahead, and those that invest in their robotics potential now will be the first to reap the commercial benefits.
(Disclaimer: Krishna Rangasayee is the CEO and founder of SiMa.ai. Views are personal.)