Q: What is the Bharat NCAP?
The Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP) is a novel safety assessment initiative introduced by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in India. It focuses on evaluating the safety performance of passenger vehicles that can accommodate up to eight passengers and have a weight not exceeding 3.5 tonnes. The program is designed to align India’s safety standards with those of countries like the US, Europe, Japan, Australia, and Latin America, all of which have their own NCAPs. Through crash tests and point-based evaluation, vehicles will be assigned star ratings, with the highest rating being five stars.
Q: Why is the Bharat NCAP rating important?
The Bharat NCAP serves as a consumer-centric platform enabling car buyers to make safer choices based on the star ratings of vehicles. It also encourages healthy competition among original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in India to produce safer vehicles. Globally, road traffic injuries are a leading cause of death, particularly among individuals aged 15 to 49 years. Annually, approximately 1.3 million lives are lost due to road traffic accidents. The program aims to address this issue, given that over 90% of these fatalities occur in low- and middle-income countries. India holds a significant portion of these fatalities, accounting for about 11% of global road traffic deaths.

Q: How are the safety ratings of vehicles determined?
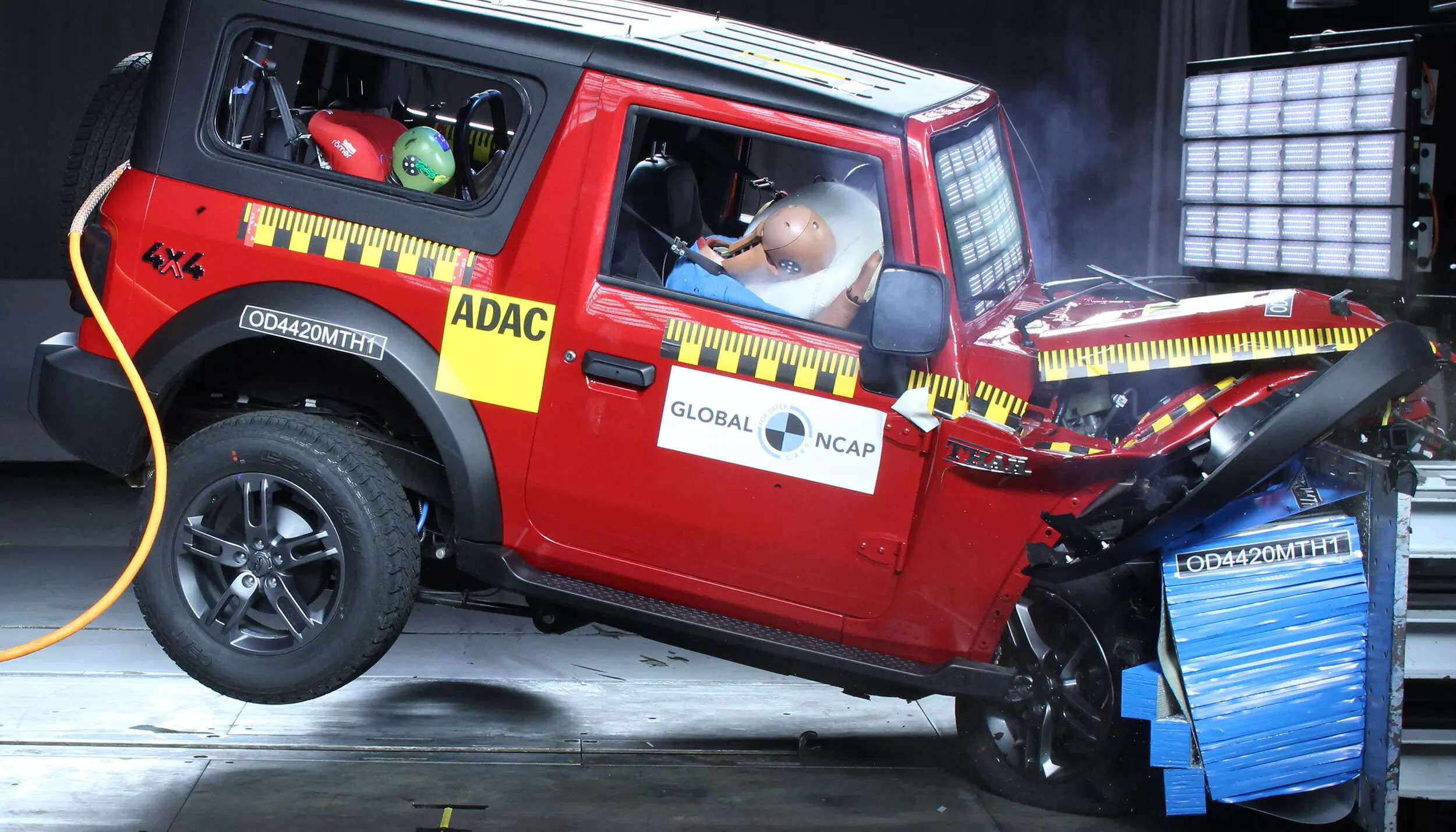
The safety ratings of vehicles are determined through a series of crash tests, including frontal, side, and pole-side impact tests. The frontal crash test is conducted at a speed of 64 kmph, while the side and pole-side tests occur at 50 kmph and 29 kmph, respectively. Ratings are assigned based on two criteria: Adult safety for front passengers and child safety at the rear. For adult safety, a car needs to score a minimum of 27 out of a maximum of 32 points to achieve a 5-star rating.
Similarly, a 5-star rating for child safety is granted to vehicles scoring at least 41 out of 49 points. Additional points are awarded for features such as ISOFIX anchorages, which contribute to child restraint systems.
Q: Is participation in the Bharat NCAP mandatory?
The Bharat NCAP is not mandatory, even in developed countries where similar programs are largely voluntary. NCAPs are designed to encourage manufacturers to go beyond basic safety standards and promote competition in incorporating advanced safety features. For instance, to attain a minimum of 3 stars, vehicles need to be equipped with electronic stability control and curtain airbags, features that are not required for basic approval.
Several manufacturers have already begun including these features as standard in anticipation of the program’s launch, such as Hyundai’s Exter and Kia’s Carens. Maruti, too, now provides electronic stability control as a standard feature in many of its cars.
Q: How did Indian OEMs test their cars before Bharat NCAP?
Vehicles manufactured by Indian automakers were tested under the Global New Car Assessment Program (GNCAP) before the introduction of the Bharat New Car Assessment Program, making it a much more lengthy and expensive process.
In the past, Global NCAP evaluated cars using only a single test for frontal crashes. This test, known as the (Front) Offset Deformable Barrier (ODB) test, consisted of colliding a vehicle into a deformable barrier at a speed of 64kph with 40% overlap. Although the frontal crash test maintains consistent speed and offset percentage, Global NCAP has tightened its criteria for determining the chest load measurements on the crash test mannequins ever since.