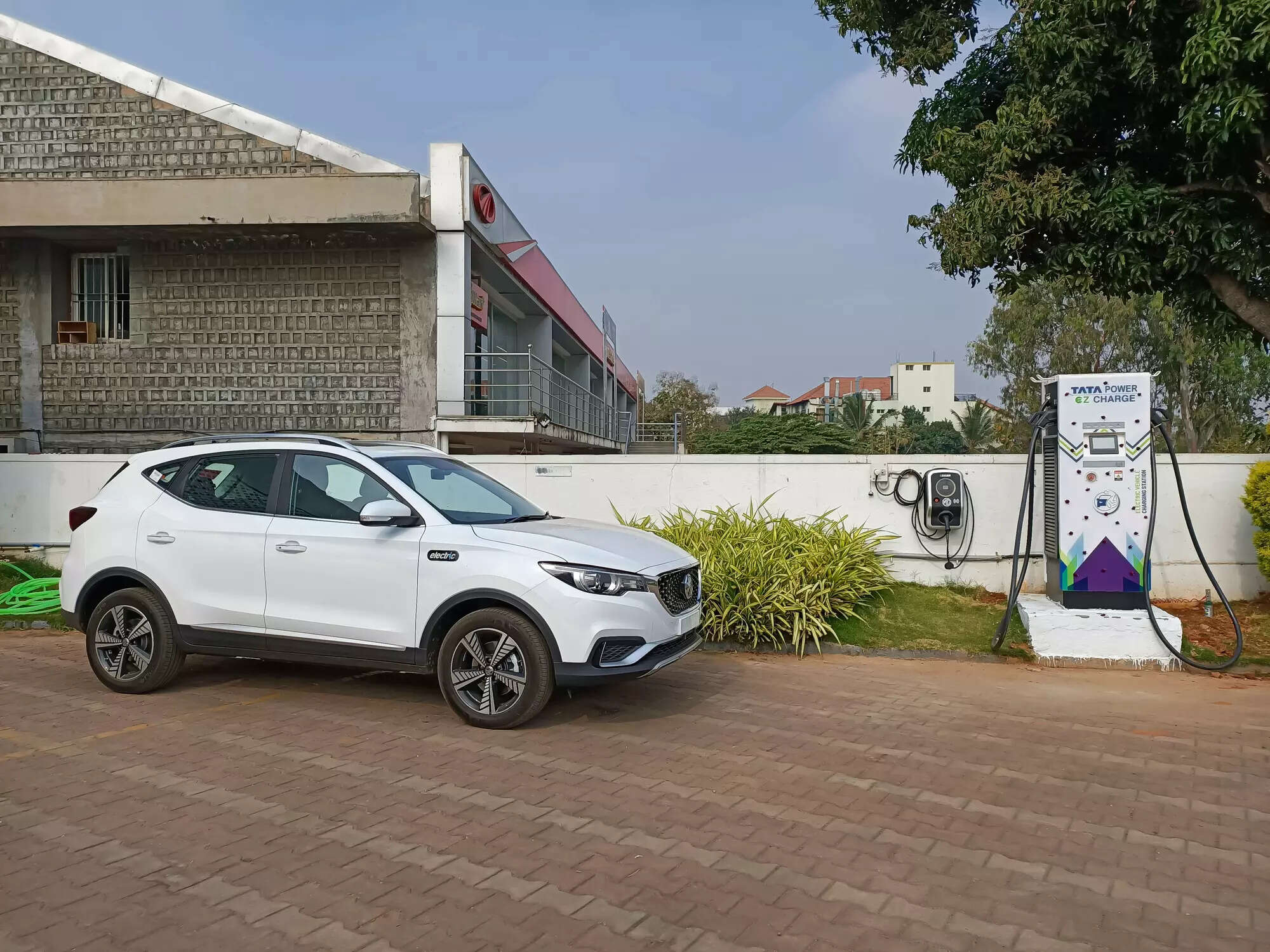
Most of the excitement in the automotive sector may be around electric vehicles, but sales of hybrids and CNG-powered passenger vehicles too are increasing at a quick pace, outpacing the industry growth.
The share of hybrids in total passenger vehicle sales in India has rose to 11.5% from 8.13% in three years, show data collated by Jato Dynamics. CNG now powers 10.3% of the new vehicles sold in the market, against 6.4% three years ago.
Petrol is still the fuel of choice for as much as 60% of buyers, followed by diesel at 16%. But the share of the two fossil fuels in the overall mix is reducing.
Electric vehicles may be the fastest growing in sales, but they account for just 1.6% of the passenger vehicle market. Adoption of EVs is constrained by two factors: high cost of acquisition and poor public infrastructure for charging the vehicles. Hybrids, which use both an electric motor and fossil fuel, address the range anxiety of the consumer, while also being environmentally more sustainable and lower on fuel consumption than fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Industry experts expect their sales to continue to grow at a fast clip.
“The compelling reason for the hybrid technology is that there is no ‘range anxiety’ as it can run on battery or gasoline. Charging infrastructure inadequacy is therefore not an impediment as these are self-charging vehicles,” said Shashank Srivastava, senior executive director at Maruti Suzuki which sells both CNG and hybrid cars.
Hybrids also offer great fuel efficiency and low running cost. In fact, depending on the driving conditions, strong hybrids work on battery alone almost 40% of the time, said Srivastava.
Strong hybrids are yet to take off and currently account for just 0.001%. But they hold significant promise, say experts.
Maruti Suzuki sells a strong-hybrid version of the Grand Vitara SUV.
A recent study conducted by the Engine Research Laboratory at IIT-Kanpur to evaluate the lifecycle emissions and total cost of ownership for battery electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles and internal combustion engine vehicles available in India showed that in the current scenario, the total cost of ownership of battery EVs was lesser than hybrids. But that was primarily due to lower tax — battery EVs are taxed at one-tenth of hybrids.
But the study stated that the current lower taxes and subsidy schemes applied on battery EVs were unsustainable in the long term and would be removed due to the huge financial burden to the government. Once a level playing field is established, hybrids would become an economical and environmentally sustainable powertrain option. This could also influence the production strategy of automakers, said experts.
“OEMs (automakers) need to consider the total cost of ownership and profitability of each option when deciding which ones to focus on. The availability of infrastructure and support for different propulsion options can also influence their adoption and profitability,” said Ravi Bhatia, president of Jato Dynamics.
Given the regulatory burden on diesel, automakers are challenged to decide their long-term strategy to contain diesel. Electric vehicles also face several friction points. This leaves the companies no other choice but to focus on petrol, full hybrids and CNG, he said, adding: “Our research and data reflect that these three options would continue to dominate in near future.”