New Delhi: Automobile exports in the first half of FY 2023-24 declined 17.5% to 22.11 lakh units. The industry shipped 26.80 lakh units in H1 FY 2022-23.
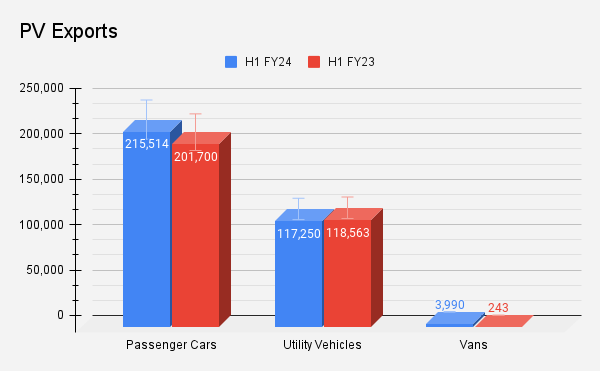
The numbers were down for all the segments including two wheelers, commercial vehicles (CVs) and three wheelers. However, the passenger vehicle (PV) segment marked a growth of 5% during the period under review.
According to Vinod Aggarwal, President, Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), “Exports volumes have seen a drop owing to the ongoing geopolitical issues and foreign exchange (forex) crisis in key export markets. The growth in the PV segment may be attributed to its export markets having a widespread region.”
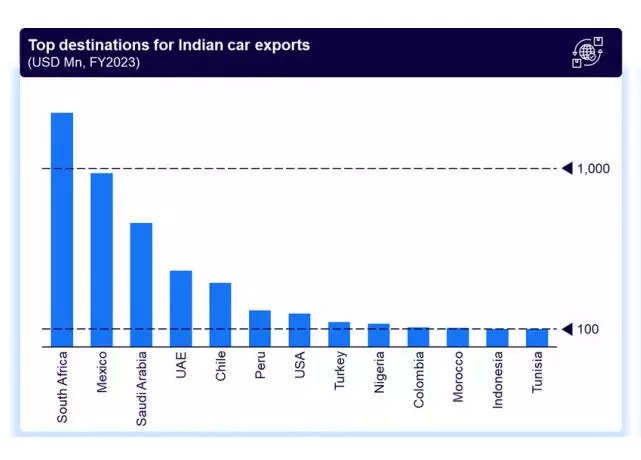
The biggest auto export markets from India are Latin America, Southeast Asia, Africa and the Middle East. However, some PV makers export to Europe and the developed markets as well.
Aggarwal added that SIAM is hopeful that the situation will improve going forward, as “a lot of work is going on to push the rupee trade by the government. Let us hope we will see some more concrete action on that.”
He suggested that even though consumer demand exists in the export markets, the challenge of availability of foreign exchange reserves is limiting the sales of vehicles because countries are focusing more on imports of essential items.
In the last quarter, some OEMs reported delays in shipments as well, however Aggarwal stated that the issue is resolved now.
Source: SIAM
Passenger Vehicles
While exports for passenger cars increased in H1 on a year-on-year basis, there was a marginal decline for SUVs.
Maruti Suzuki, the top car exporter in the country, has significantly grown its shipments in the past two years. Currently, it exports 18 models to about 100 countries. The company’s key export markets include Africa, Latin America, Asia and the Middle East. In October, it also started exporting its 5-door Jimny.
Shashank Srivastava, Sr Executive Officer, Maruti Suzuki anticipates the export momentum in the segment to continue in the second half of the year as “exports largely depend on different geographies and the markets where we export are not under major challenge.”
The automaker expects a 5% YoY growth for its total shipments by the end of FY24.
Recently, Nikkei reported that Japan’s Suzuki Motor will start producing electric vehicles (EVs) in India and export them from there to Japan as early as 2025. It is reportedly expected to set up a new production line at a plant in Gujarat, where Maruti Suzuki would start producing next autumn.
Top 5 PV Exporters
Hyundai Motor India exports from its plant at Sriperumbudur in Tamil Nadu. The maker of Creta SUV ships its vehicles to over 85 markets, including left-hand drive (LHD) and right-hand drive (RHD) countries. Its biggest export markets include South Africa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Chile, Mexico and Peru.
Tarun Garg, COO, Hyundai India said the company’s export volumes have increased “due to introduction of the new Accent (new Verna in domestic market), Grand i10 5-door facelift (Nios in domestic), Grand i10 4-door facelift (Aura in Domestic), and the Venue LHD in the respective markets.”
The company exported an average of over 14,000 units every month this year. “2023 has witnessed a strong momentum for Hyundai exports. We are closely monitoring the geopolitical situation especially in the Gulf region and will make market adjustments as we deem necessary,” Garg said.
Experts suggest that while there are global issues including inflation, energy crisis, oil prices, availability of forex reserves, and political conflicts, which impact the overall business, specific challenges for the shipments in this segment are not expected.
According to a recent report by Arthur D. Little consultancy, India which is presently the fourth-largest automotive market in the world, valued at USD 250 billion has the potential to emerge as a USD 1 trillion export powerhouse, leveraging its favourable position as an alternative to China, as part of the global industry’s China-plus-one policy, to manufacture global electric vehicles, as well as establishing its dominance in automotive software research and development.
Developing its global competitiveness and reliance as a manufacturing hub will position India at par with Japan, Germany, and South Korea, which are global hubs generating over USD 500 billion annually. The report said that while India’s exports predominantly serve emerging markets, many OEMs find the manufacturing standards below par for its developed market clienteles. Recent safety and emission regulations are, however, narrowing the divide between the local automotive industry and developed economies.
It also noted India’s strengths, including its thriving domestic market, and suggests that global players should deepen their presence in India for manufacturing, sourcing, and software. Indian companies, in turn, have the potential to become global champions with significant international reach as the global automotive industry undergoes major disruptions.
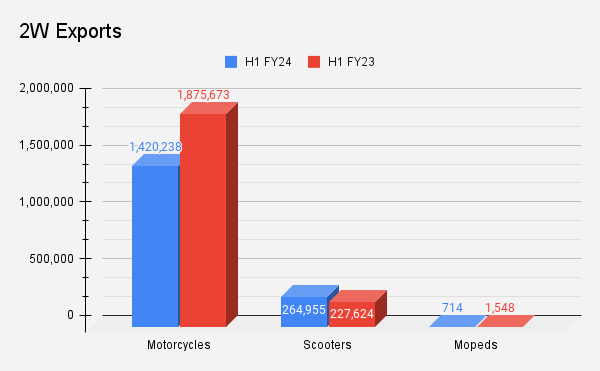
Two Wheelers
Export volumes in the two wheeler segment dropped 20% YoY to 16.85 lakh units in H1 FY24 when compared to 21.04 lakh units in H1 FY23. The country’s largest two wheeler exporter Bajaj Auto witnessed a YoY drop of 22% during the period.
Export scenario for two wheelers started deteriorating in Q2 FY23, which then progressively dropped down around Q3 and Q4 FY23.
“Exports are taking their due course to recover as foreign exchange remains the biggest challenge. A lot of countries are also still reeling under very significant macroeconomic challenges,” Dinesh Thapar, CFO, Bajaj Auto said in the company’s post earnings call.
There is a ban happening in Iraq, a civil strife and an uprising in Sudan, which have prevented anything to be shipped over there. There is also a raging inflation in a lot of these countries. There has been a fuel price hike in Bangladesh, devaluation in countries like Kenya, Nigeria. There is global unrest owing to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. But the devaluation of currency and availability of foreign exchange still remain the biggest challenge.
During Q2 FY24, Bajaj said it managed to build back a part of the inventory in some markets. “This is not necessarily a reflection of a significant positive shift in the operating or retail environment in those countries, but the fact that we have been able to arrange for foreign exchange. Though it still remains a challenge on-ground.”
Top 5 2W Exporters
Africa accounts for half of Bajaj’s total exports from India. Within Africa, Nigeria takes up about half of the company’s total exports.
Over the last quarter, it has seen a little positive momentum happening in markets like Mexico, Central America, and Turkey. Thapar estimates improvement in export volumes during H2, but the recovery will likely get pushed to FY25.
Commercial Vehicles
Export volumes in the commercial vehicle segment declined 25% YoY to 31,864 units in H1 FY24, when compared to 42,306 units in H1 FY23.
Within the segment, both the categories of medium and heavy commercial vehicles (M&HCV) and light commercial vehicles (LCV) were on a decline.