In India, electric cars have been too costly for many. But when Tata Motors launched its Tiago EV (electric vehicle) earlier this week, it lowered that hurdle and posed a challenge to rival carmakers to line up matching offers.
With the Tiago EV’s starting price of Rs 8.49 lakh, the price gap between a conventional internal combustion engine car and its electric version in India has narrowed enough to coax all those who had put their electric car plan on the back burner to go for it.
The launch is also seen sparking fresh competition in the country’s passenger vehicle (PV) space, as rival carmakers will have to tweak pricing and parameters of their electric products to match Tata Motors’ offer.
Tata Motors is the leader in the Indian electric PV segment with its Nexon, Tigor and Tiago. It will see competition from Maruti Suzuki, Mahindra & Mahindra, Hyundai and Kia, and Chinese major BYD, which are lining up new launches. Experts say the Tatas may find it tough to maintain this lead.
Analysts say EV players in India are seeing considerable interest from tier 2 and 3 towns, promoting original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and financiers to drive into such markets.
Electric PVs, which have the lowest penetration in the country’s automotive sector, are expected to see faster adoption among fleet operators, taxi aggregators and government agencies.
In comparison, electric two- and three-wheelers are seeing faster adoption as these segments account for about 80% of the domestic automobile volumes.
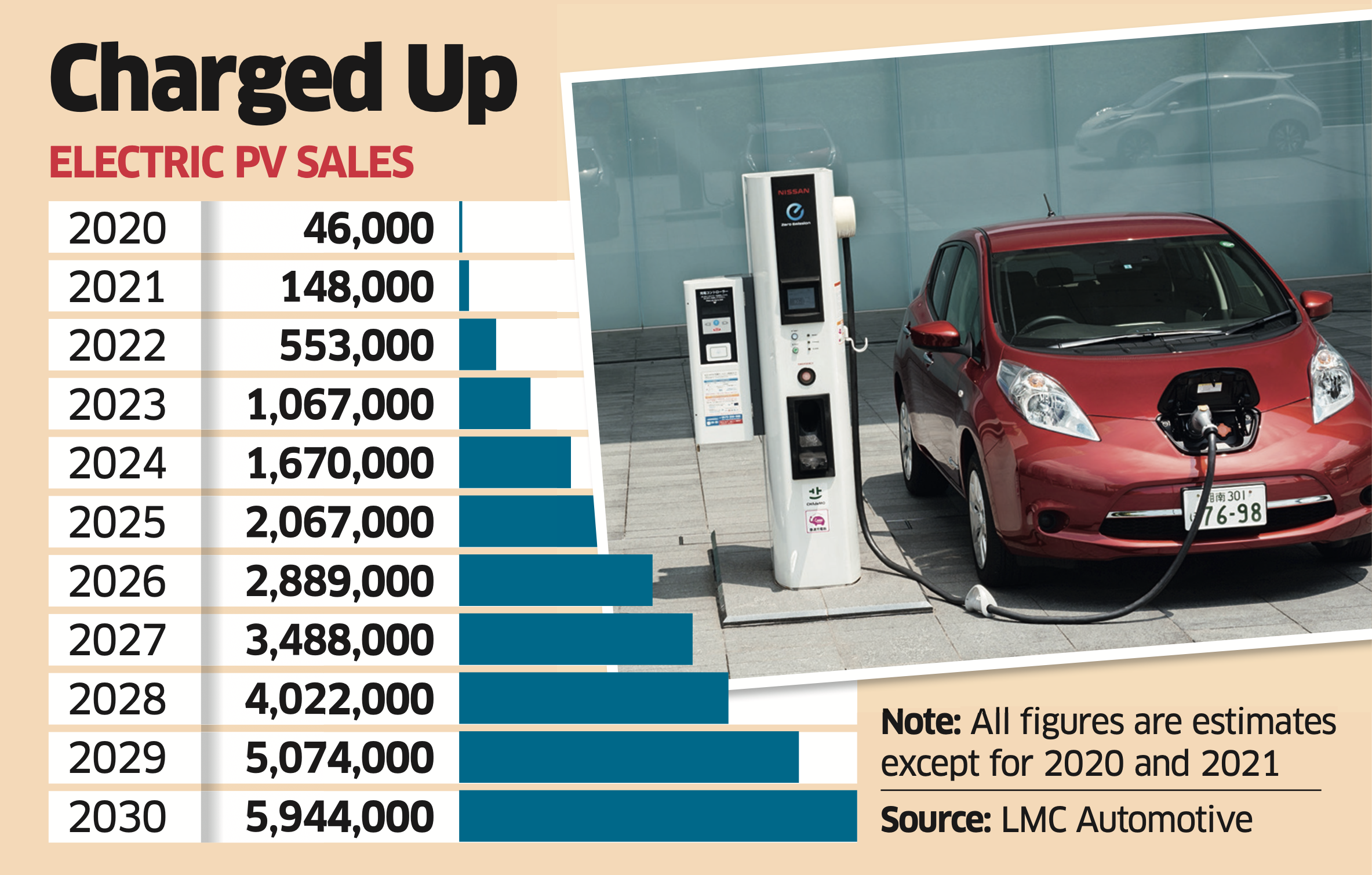
By 2030, the top EV sellers by volume in India’s PV market will be Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki, Mahindra & Mahindra, Hyundai and Kia, according to LMC Automotive, a consultancy firm.
TURN HEADER
‘EV Mkt Share to Top 13% by 2030’
While Mahindra plans to expand its EV portfolio aggressively in only one segment — SUVs — Tata Motors and Maruti Suzuki will have EVs in both sedan and SUV segments, which will give them more opportunity to grow and expand volumes, said Ammar Master, senior analyst at LMC Automotive.
According to LMC Automotive, the share of electric in India’s PV segment would increase from 0.2% in 2020 to 5.5% in 2025 and 13.5% in 2030.
“We are opening EV outlets in 80 cities in India to make EVs more accessible,” said Shailesh Chandra, managing director of Tata Motors Passenger Vehicles and Electric Mobility. “In the last five months of this financial year, the industry has sold about 20,000 EVs. Expect industry to cross 55,000-60,000 by the end of FY23. We cover 88% of this market so far and we aspire to end FY23 with the 50,000 sales mark.”
LMC Automotive’s Master said that as more players enter India’s electric PV market, the firm foresees Tata Motors’ market share in the electric PV market declining to around 40% by 2030, and more rapidly in 2024-2025, after Mahindra, MG Motor, Hyundai and Kia introduce new EVs.
A further disruption is anticipated in 2026 when Maruti Suzuki enters the electric PV market. The country’s largest car maker is not expected to have any EV models before the end of 2025. Its first EV is expected to be a B-segment SUV. According to Master, it will be the only Suzuki EV in the market before the OEM starts to add EV versions to some of the company’s existing models from 2029.
Maruti Suzuki is now focusing on developing hybrid technology before moving up the technology curve to battery electric vehicles. The company expects the penetration of electric PVs in India to be in the 15-17% range by 2030.
Shashank Srivastava, the carmaker’s senior executive director for marketing and sales, said although the cost of acquisition is less of a barrier, charging infrastructure and range anxiety continue to be a challenge.
According to LMC Automotive’s estimates, EVs will account for almost 40% of Tata Motors’ PV sales by the end of this decade. For the same period, EVs will account for about 20% of Mahindra’s PV sales, and will be 8% each for Maruti Suzuki and Hyundai.
Vikram Kirloskar, vice chairman of Toyota Kirloskar Motor, said penetration is going to grow geometrically for electric passenger cars. His company will soon launch electric PVs at competitive price points as the local content is expected to be high.
India’s taxi fleet market is seeing good traction for EVs and companies like Tata Motors are firming up plans to tap into this demand. In tie-up with BluSmart Mobility, Tata Motors plans to expand its all-electric fleet across the national capital region.
The shared mobility market is opening up rapidly and players like Uber, Ola Cabs, BluSmart and Meru are opting for more EVs in their fleet, as the low cost of ownership in addition to safety and passenger comfort makes it an attractive proposition.
BluSmart, which has a full-electric fleet, hopes to add some 4,000 vehicles by the end of December 2022 and expand it to 25,000 by December 2023. “While we are expanding the fleet, we will not expand the geographies,” said Anmol Jaggi, founder of BluSmart. “Will try and satisfy existing geographies of Delhi and Bengaluru.”
A spokesperson for Uber said, “We are committed to aggressive sustainability goals globally as well as in India. Through various means, be it incentivising EV switch for drivers, policy advocacy or supporting ecosystem development, we are committed to make the EV transition in India.”
Uber has 5,000 EVs on the platform, of which the majority are two-wheelers.
An email query sent to Ola remained unanswered till as of press time.
“We are committed to the government’s vision of 30% EV penetration by 2025 and are working towards it,” said Chandra of Tata Motors.