New Delhi: India is the number one in the world in road accidents. The majority of vehicles involved in crashes in India are passenger cars (30%), followed by motorcycles (24%), trucks (22%), and buses (21%). Commercial vehicles such as trucks and buses are involved in half of all pedestrian accidents, and pedestrian injury risk is high in India, with 99% of pedestrians are susceptible to injury.
Released during the 7th UN Global Road Safety Week, (May 15-21, 2023), the findings are part of a study by technology provider Bosch. It analyzes pedestrian behaviour in India to understand the characteristics of pedestrian crashes in India and to identify counter-measures that can improve road safety in India.
According to the report, about one in every ten traffic-related fatalities in the country is a pedestrian. In 2021, the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) registered 68,053 pedestrian crashes in 2021, which contributed to 16.5% of the total accidents that year.
Girikumar Kumaresh, Principal Advisor Road Safety, Future Mobility & Expert Accident Research, Bosch India, said that certain products which are designed for the European market fit for our country as well because they are about 20 years ahead of us. However, we need India-specific products considering the infrastructure design, and the differences in driver and user behaviour.
Giving an example, he noted that in India, there are people sleeping on the roads. These components are very unique to India and nowhere in the product designs of entire Europe.
“During the past decade, infrastructure and vehicles have been of best quality in India. However, we have not understood the needs of the road users. We have to borrow the best techniques from the Western world, understand the right usage and the pedestrian behaviors from the Eastern and balance both in India to distribute it to the entire world,” he told ETAuto.
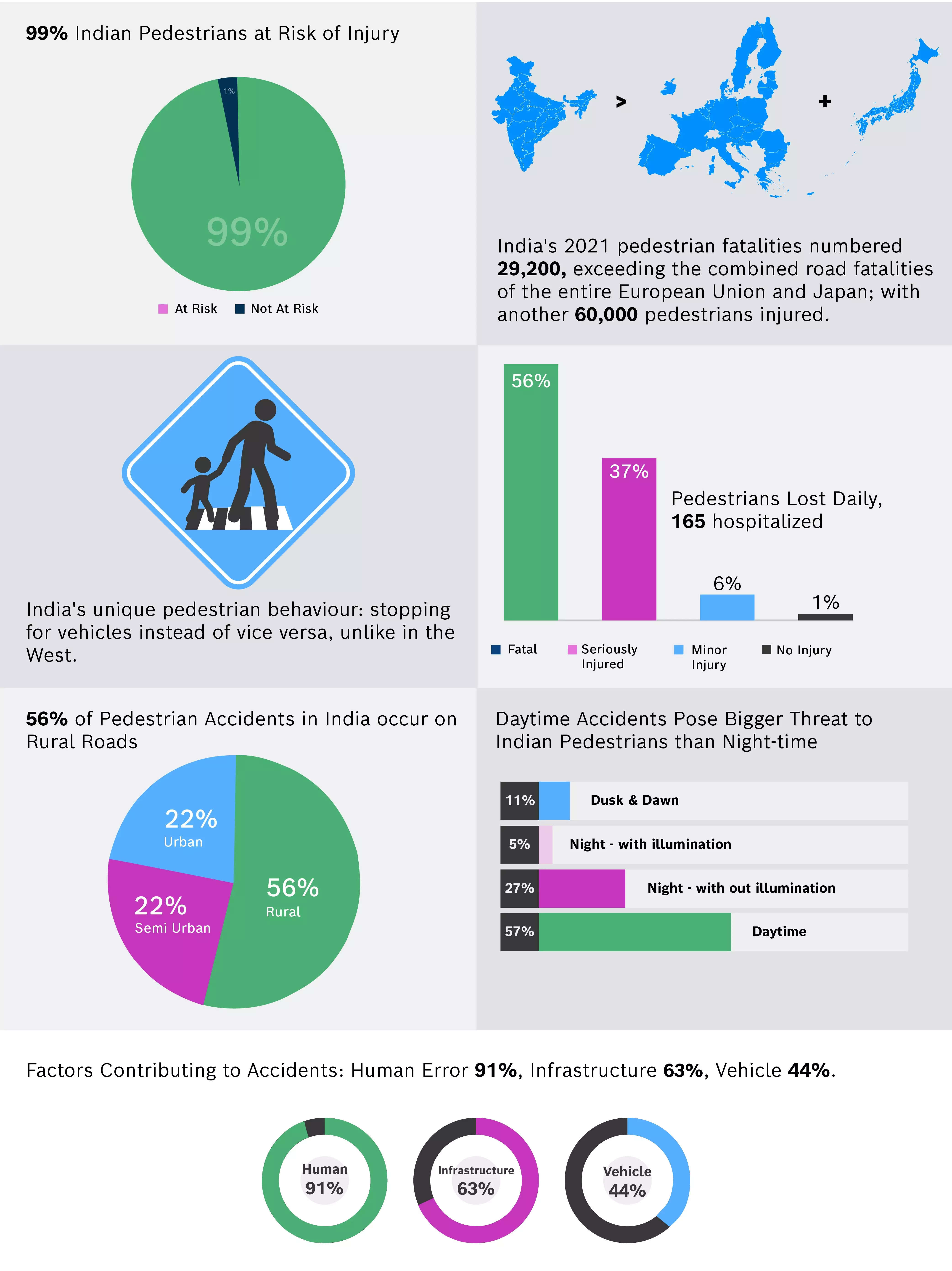
The report also found that human error is the leading contributor to pedestrian accidents in India, followed by infrastructure and vehicle-related factors. Each accident has a multi-level contributing factor from either human, infrastructure, and vehicle or all combined together. Human error contributed 91%, infrastructure 63% and vehicle 44%.
Human factors such as dangerous behaviour on the roadway, violation of right of way, walking on the roadway, alcohol influence, illegal pedestrian entry, and careless crossing are major causes. Infrastructure issues include the lack of pedestrian crossings, poor walking facilities, and inadequate warnings about accidents or parked vehicles. Vehicle issues include Illegal alterations such as bull bars, protruding cargo, and cargo not secured in commercial vehicles, as well as poor braking efficiency, are major vehicle-related concerns.
The report stated that pedestrians are at high risk in traffic accidents, with the front of the vehicle being the most common point of impact. There are now stricter legal requirements and consumer protection tests for pedestrian safety, and various active and passive safety systems have been developed to mitigate pedestrian accidents. These include the Pedestrian Protection Airbag, Active Hood Lifters, and Predictive Pedestrian Protection system.
Predictive emergency braking system: (AEB Pedestrian) detects the distance to the pedestrian in front and it prepares the braking system for potential emergency braking. If the driver fails to react to the critical situation, the system can automatically initiate full braking in an attempt to prevent the collision. The technology used is the fusion of radar sensors and the multipurpose cameras.