By Abishek Narayanan
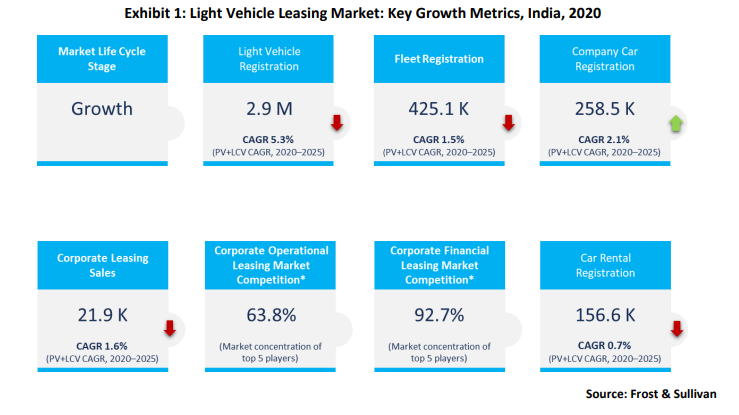
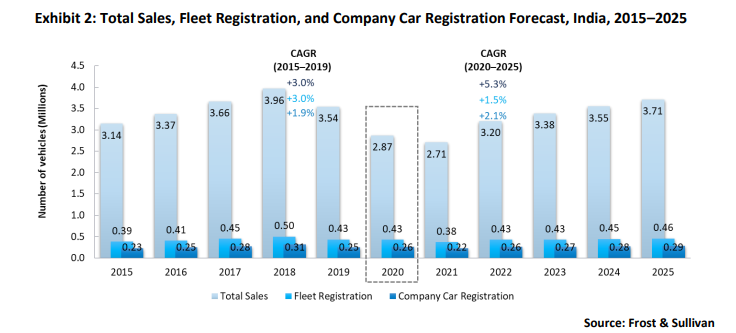
In 2020, registration of light vehicles, including passenger vehicles (PVs) and light commercial vehicles (LCVs), in India were pegged at 2,866,996, 19.1% less than in 2019, mainly owing to the economic slowdown and the COVID-19 pandemic. Company car registrations remained resilient with a marginal growth rate of 2.5% in 2020 compared to the previous year. However, this number was well below 2018 levels due to the delayed fleet renewals. Thus far, outright purchases have dominated the Indian company car market with more than a 91% share in company car fleets from 2015 to 2020, as leasing solutions are still at a nascent stage in the country. The negligible presence of the company car concept and low awareness are the major reasons for the low uptake of leasing in the Indian automotive market. In addition, the travel needs of users are dominated by two-wheelers rather than cars. The xEV (including battery-operated electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids, and hybrids) leasing market held an insignificant share in 2020. It is expected to gain traction over the next decade due to government support and investment from leasing companies. The Indian light vehicle leasing market is concentrated, and the top five participants accounted for a combined 63.8% share in the operational leasing segment in 2019; in the financial leasing segment, the top two companies accounted for a combined 87.2% share.
Market drivers
- The Indian light vehicle leasing market is still in the early growth stage and holds substantial potential for growth. The B2C segment will mainly drive demand.
- Operational leasing will become corporates’ preferred option as it minimizes the time, expenses incurred for maintenance, and also provides tax benefits as the payments for lease vehicles qualify as operational expenses in balance sheets.
- The vehicle scrappage policy to phase out vehicles older than 15-20 years will limit supply in the used car segment. This will benefit leasing companies as they will obtain a higher resale value for cars in the secondary market.
- SMEs will continue to draw attention and, if rightly capitalized, a fair share of revenue will be channeled through this sector to leasing firms. This is part of many companies’ strategies, including PumPumPum, a flexible, affordable and convenient solution for car ownership.
- The Indian government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme will play a major role in reducing the cost of auto components by encouraging self-reliant production through incentives. The benefits of effective cost reduction will help leasing companies increase the number of contracts at an affordable price to their customers.
Market restraints·The concept of company cars is almost negligible in India, and awareness of leasing vehicles among the public is low. These factors will significantly impede the market growth.
·The ongoing health crisis, which has forced companies to offer a work-from-home option for employees, has severely hit leasing companies as it has resulted in delayed contract renewals. Commercial vehicle leasing will remain resilient compared to passenger vehicle leasing due to a significant rise in last-mile deliveries.
·The global semiconductor shortage will continue to put pressure on India’s vehicle production and impact leasing companies’ procurement of new vehicles.
·The costs associated with private leasing are higher than the costs linked to vehicle ownership. This will keep potential Indian customers at bay, many of whom are gradually moving away from vehicle ownership, which has traditionally been considered a status symbol.
Top three strategic imperatives for the Indian light vehicle leasing market
1. Competitive Intensity – Emergence of New Mobility Solutions: Car subscription services are emerging as major competition to private leasing. Subscription services offer great flexibility; for example, contract periods can be as low as six months. Leasing companies should consider the provision of flexible contract periods at low costs. This will drive sales as leasing vehicles come with a non-commercial plate, which allows personalization and the option of buying the vehicle at the end of the contract period (unlike subscription vehicles).
2. Geopolitical Chaos – The China Plus One Strategy: The US-China trade war affected many companies, and some of them are shifting their manufacturing units (either partially or fully) to India. The Indian government’s PLI scheme complements the country’s strategic location and skilled labour force. The increased localization in the automotive industry will further reduce vehicle costs when supply is sufficient. This will happen in the long term, aided by the government’s PLI scheme. Leasing companies will pass on the cost benefits to customers.
3. Customer Value Chain Compression – Digitalization: The COVID-19 pandemic and related lockdowns have restricted customers from visiting showrooms and performing test drives. Automotive/leasing companies are feeling the heat, thanks to the rapid growth of digitalization. The rapid construction of digital platforms/infrastructure is needed. Online documentation, virtual tours of showrooms, and pick-up and drop-off facilities for test driving can add value to services.
Total market and company car analysis
The economic slowdown and the government’s increasingly stringent emission norms decreased overall vehicle sales in 2020. In addition, the price increases due to BS VI norms resulted in a weak buying sentiment. The COVID-19 pandemic affected the auto industry, which has faced headwinds in terms of semiconductor shortages and supply chain issues. Total company car registrations accounted for 9% of total vehicle sales (PVs+LCVs) in 2020, compared to 7.1% in 2019. Fleet registration is expected to remain muted due to delayed renewals by companies whose offices remain closed and prevailing uncertainties over lockdowns.
Corporate leasing market
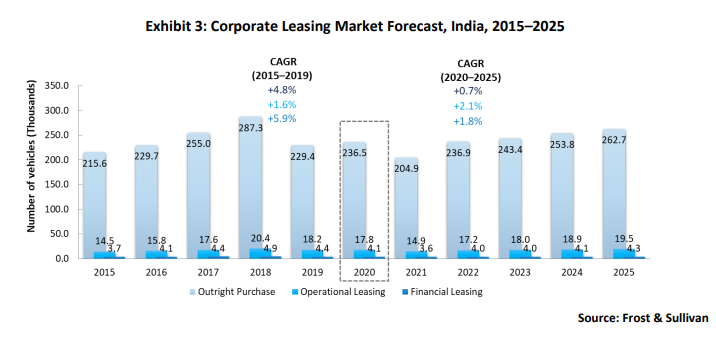
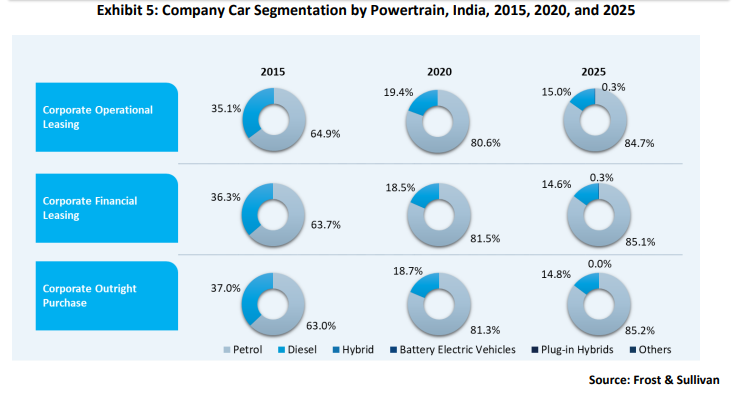
The Indian company car market is concentrated, and outright purchases accounted for a 91.5% share in 2020. All three segments are expected to post a slow growth rate and are unlikely to surpass 2018 levels, even by the end of 2025, as the pandemic has dealt a heavy blow to an already weak automotive sector. Moreover, the B2B market for leasing is negligible compared to the B2C segment. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of company cars from 2020 to 2025 is expected to be 2.1%. Job losses due to the pandemic are a major factor contributing to slow growth. Operational leasing is in the nascent growth stage and has a lot of ground to cover. The financial leasing market has an insignificant presence in the country as operational leasing is popular and companies focus on operational leasing to grow.
Private leasing market
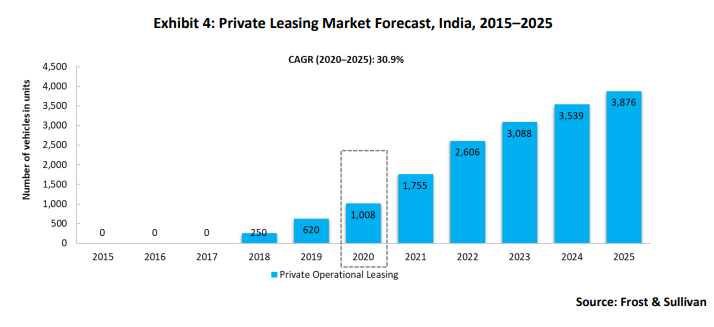
Private leasing registrations nearly doubled in 2020 compared to 2019, indicating the emergence of a new business model in India’s mobility sector. Operational leasing will continue to dominate the private leasing segment as market participants take cues from the success of this business model in European countries. By 2025, it is expected to grow nearly four times from 2020 levels. Cost-effective products, increasing customer awareness, and dealerships’ private leasing promotions will be the key long-term growth drivers.
Powertrain segmentation in the light vehicle leasing market
Although the government initiatives will drive the use of EVs in the country, significant challenges exist. Better charging infrastructure, affordable EVs in the price-sensitive Indian market, tax incentives for manufacturers, and subsidies on EV purchases will spur demand. EVs were finding their footing in the leasing segment when the pandemic hit. Subsequently, EV use in this segment declined as these are costly vehicles, and customers were reluctant to make expensive purchases during a crisis. However, when the pandemic subsides, sales are likely to pick up, and the market should be ready for this scenario.
Rental market
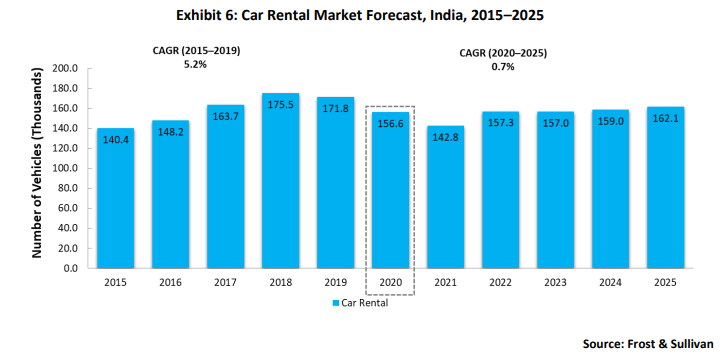
The COVID-19 pandemic, which has accelerated the work-from-home job format, has severely affected the car rental industry’s growth (the majority of which is attributed to corporate travel). Although the rental industry is set to return to a CAGR of 0.7% from 2020 to 2025, it is expected to show greater resilience than the leasing market because it is anticipated to revive after pandemic-related restrictions are completely lifted, and airports become fully operational. The volatility and fluctuations in the rental business are higher, and these are significantly associated with economic health.
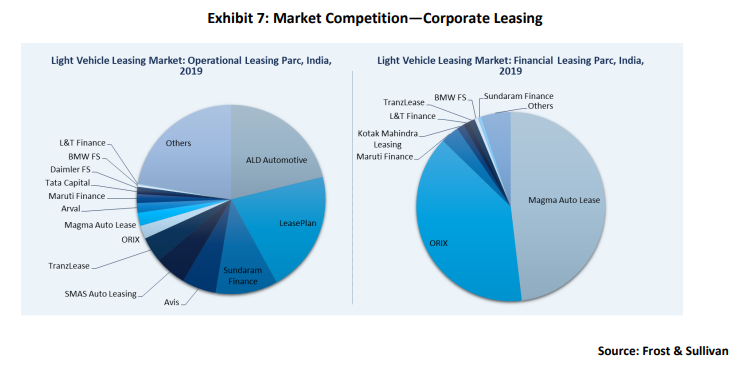
Market competition: corporate leasing
The operational leasing market is concentrated, and the top five companies accounted for a combined share of 63.8% in 2019, while the other participants tried to sustain themselves with shares well below 5% each. Magma Auto Lease and ORIX held a substantial share of 87.2% in the financial leasing market, although the segment only accounts for one-fifth of the vehicles compared to four-fifths for the operational leasing segment. Strategic partnerships with OEMs will be critical to industry growth. Some examples of partnerships are ALD’s tie-up with Hyundai and Citroen and ORIX’s collaboration with Maruti Suzuki and Skoda India.
Growth opportunity 1: Awareness and affordable pricing for private leasing
Private leasing holds substantial potential as millennials are keen to explore options other than car ownership; they are eager to try out new cars without worrying about residual value. OEMs such as Hyundai and Mahindra offer their vehicles for lease; however, leasing-associated costs are likely to be high for the cost-sensitive Indian customer. Awareness of private leasing is low even in metropolitan cities, whereas it is almost non-existent in other parts of the country. India has only 22 cars per 1,000 citizens, which is significantly low considering its large population. This gap creates a good opportunity for leasing companies to offer their products and services.
Leasing companies should increase their stake in the B2C segment as private leasing will witness multi-fold growth in the long term. OEMs can leverage the option of private leasing as it will fetch revenue when their sales are down or when there is a huge unsold inventory of certain car models. Leasing companies and OEMs can use creative advertisements, test drive campaigns, and social media campaigns to boost awareness of the benefits of the product offering to potential customers. Better-priced products with flexible contracts can be considered car subscription services and will compete intensely with leasing.
Growth opportunity 2: xEV leasing in B2B for faster EV adoption
By 2030, the Indian government aims to have EVs comprise 70% of commercial cars and 30% of private cars on the roads. Energy Efficiency Services Limited is a central government institution that floats tenders to procure EVs. It also helps fleet management companies lease their EVs to government officials. Such initiatives indicate the government’s interest in the promotion of EVs. Ownership costs will remain a major hurdle for the price-sensitive Indian customer. B2B will provide an opportunity to boost EV presence, and companies will not only benefit by meeting their targets in terms of carbon footprint reduction but also retain their employees by providing vehicles for lease through salary-sacrifice schemes.
At present, the feasibility of this target is unclear, but market participants should consider the inclusion of EVs in their portfolios as this will ensure they can leverage the EV opportunities of the future. Adequate charging infrastructure is an urgent need that will provide a hassle-free end-user experience. Therefore, Frost & Sullivan recommends that market participants focus on tie-ups with providers of EV charging stations and related infrastructure to make it a win-win situation for all stakeholders involved. The B2B segment will see higher uptake of EVs, which will boost the confidence of B2C users to adopt these vehicles.
Growth Opportunity 3: Digitalization for the post-pandemic era
The ongoing health crisis has accelerated the need for digitalization; contactless services have become part of the new normal. Digitalization will significantly reduce the number of visits to showrooms. The number of smartphone users in India is projected to reach 830 million by 2022, and the number of internet users is expected to reach 900 million by 2025, which is an increase of 45% from 620 million in 2020. The need for digitalization is clear, and customers will look to avail these services from the comfort of their homes.
Frost & Sullivan recommends that virtual tours of vehicles at dealerships be increased. This is a convenient option for customers (especially in terms of saving time), and leasing companies can benefit by reaching out to a larger customer base. Leasing companies can build digital platforms to enhance the user experience. End-to-end services such as quote customization, lease contract management, and alerts for scheduled maintenance and contract renewal can be offered through online portals and dedicated smartphone applications.
Strategic partnerships can be established with firms that are experts in digital transformation and AI technologies. AI-based advertisements that target potential customers with the right products and analyse vehicle models that have the most online visits offer demand insights and help companies leverage their business models.
Conclusions and outlook
The Indian light vehicle leasing market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2020 to 2025. The growth of operational leasing in the company car segment will be slow, yet evident with the COVID-19 pandemic opening up some opportunities. Companies will hesitate to sign new contracts or renew their fleets due to the prevailing uncertainties. Outright purchase is expected to register a consistent 91% share (approximate) in the company car market until 2025. Private leasing will be a new growth opportunity in the Indian light vehicle leasing market. Operational leasing will single-handedly drive market growth as most customers are not ready to own a depreciating asset. Frost & Sullivan expects private leasing units to grow four times by 2025 from 2020 levels. The xEV leasing growth is expected to be slow due to higher costs and faster depreciation. As change is inevitable in terms of moving to a green environment, the development of adequate charging infrastructure, government incentives/subsidies, and attractive pricing will provide the initial momentum. Digitalization can be used as a tool to gear up for growth in the leasing market. Robust digital platforms will also reduce the friction with customers (in terms of the various procedures associated with leasing a vehicle). Soon, this value addition will become a necessity.
(Disclaimer: Abishek Narayanan is Research Manager, Mobility Practice, Frost & Sullivan. Views are personal)
Also Read: